Scorecard Method
scoring
credit score
scorecard
Dictionary
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Information Value (IV) | method to select important variables in a predictive model |
| Weight of Evidence (WOE) | tells the predictive power of an independent variable in relation to the dependent variable |
| Logistic regression model | is a binary classification model by using logistic concept |
Definition
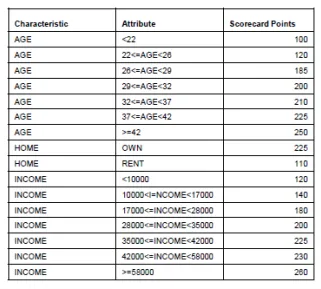
Scorecard - a model that using probabilities or ratings to assess the Risk levels associated with applicants or clients. All variables will contribute to the overall points that applicants will get.
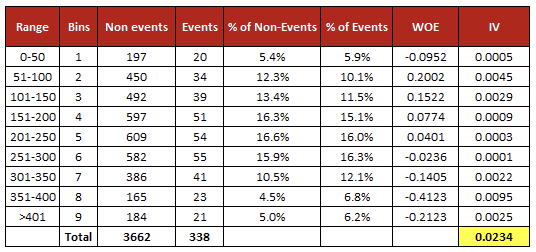
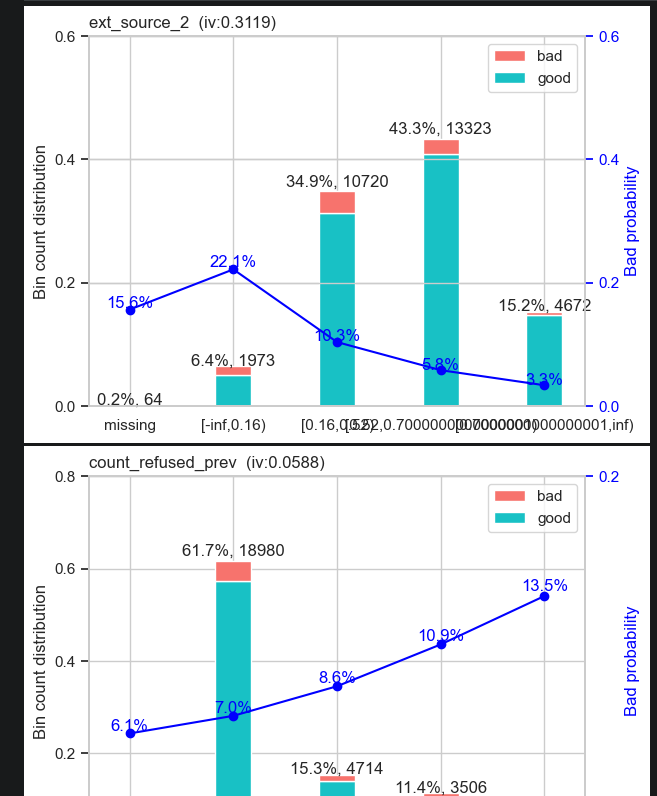
Weight of Evidence (WOE) - WOE Used to tells the predictive power of an independent variable in relation to the dependent variable. it is generally described as a measure of the separation of good and bad customers. Bad Customers refers to the customers who defaulted on a loan. and Good Customers refers to the customers who paid back loan.
WOE helps to transform a continuous independent variable into a set of groups or bins based on similarity of dependent variable distribution i.e. number of events and non-events.

- Distribution of Goods - % of Good Customers in a particular group
- Distribution of Bads - % of Bad Customers in a particular group
- ln - Natural Log
Positive WOE means Distribution of Goods > Distribution of Bads Negative WOE means Distribution of Goods < Distribution of Bads
Hint : Log of a number > 1 means positive value. If less than 1, it means negative value. some term used events for Bads and non-events for Goods.
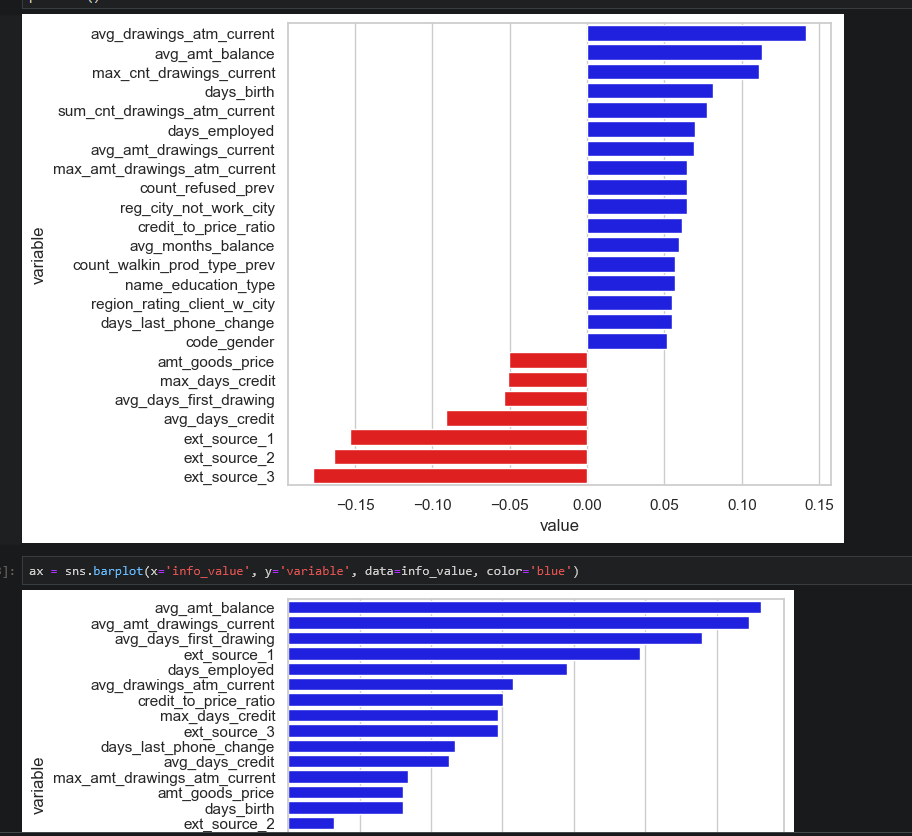
Information value (IV) - is a method to select important variables in a predictive model. It helps to rank variables on the basis of their importance.

Rules related to Information Value 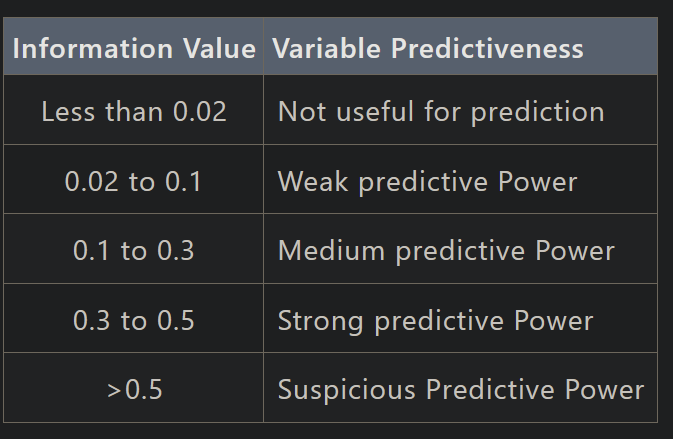
Logistic regression model - is a binary classification model by using logistic math concept. Logistic regression models take as input both categorical and numerical data and output the probability of the occurrence of the event.
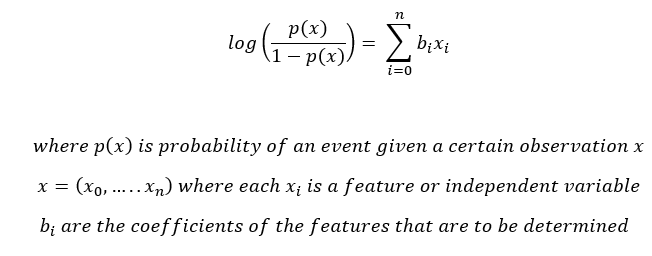
We need to predict the weights/coefficients bi such that, the probability of an event for an observation x is close to 1 if the actual value of the target is 1 and the probability is close to 0 if the actual value of the target is 0.
How to calculate
- Weight of Evidence (WOE) Follow the steps below to calculate Weight of Evidence
- For a continuous variable, split data into 10 parts (or lesser depending on the distribution).
- Calculate the number of events and non-events in each group (bin)
- Calculate the % of events and % of non-events in each group.
- Calculate WOE by taking natural log of division of % of non-events and % of events
- Note : For a categorical variable, you do not need to split the data (Ignore Step 1 and follow the remaining steps)
- Combine categorical variables with similar WOE and then create new categories of an independent variable with continuous WOE values. In other words, use WOE values rather than raw categories in your model. The transformed variable will be a continuous variable with WOE values. It is same as any continuous variable.
- If there is a monotonic trend of WOE values (either descending or ascending), then we can confirm that our bins have a general trend. If it’s not monotonic, then we need to compress the bins to form new groups and need to check the WOE values again.
Why we used it
Scorecard is the most popular credit scoring method. There are two main reasons why the scorecard is the most common form for credit scoring:
- It is easy to interpret to people who has no related background and experience such as the clients.
- The development process of the scorecard is standard and widely understood.
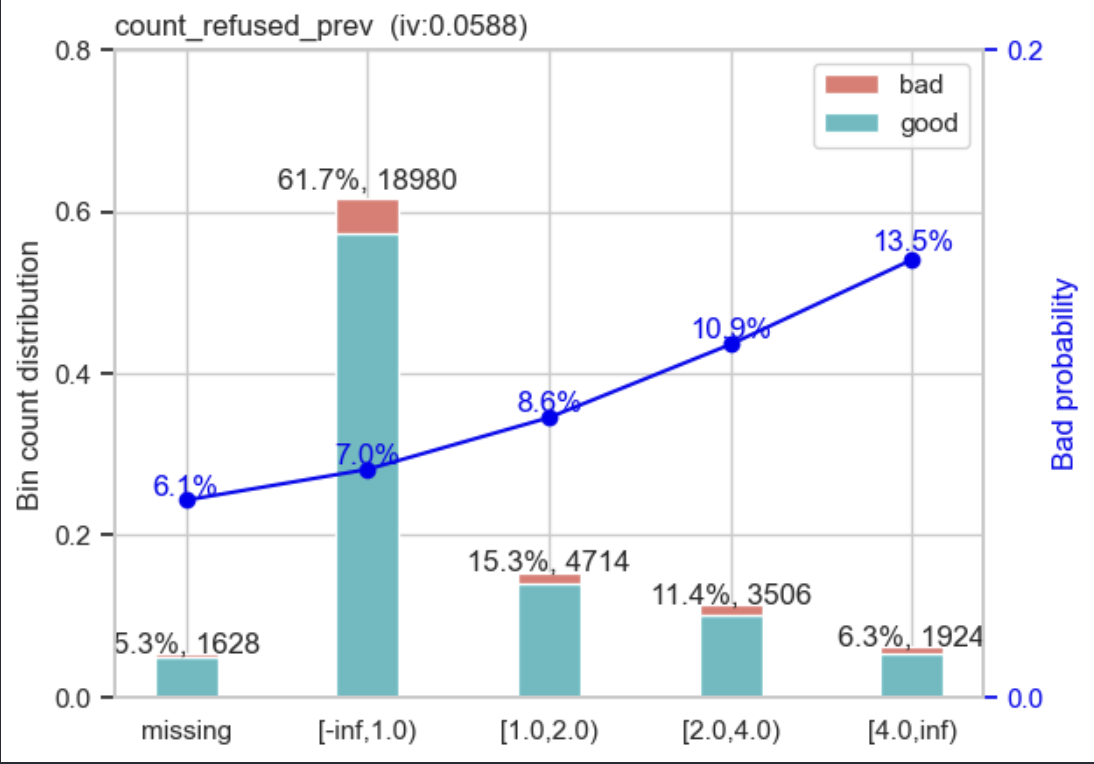
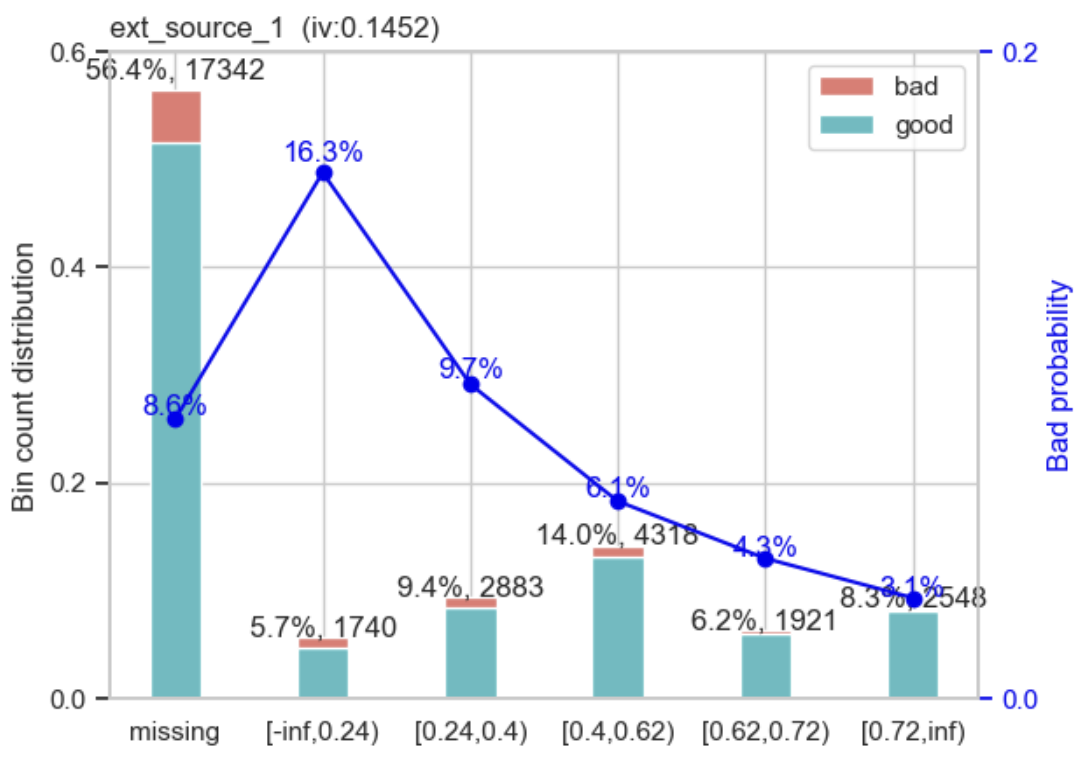
WOE will help us determine the predictive power of an independent variable compared to a dependent variable. by using the binning process to convert numerical and categorical values to specific groups to determine how well the variable can separate an event from a non-event.
IV will help us to determine how important value for each variables in a predictive model. by using this method, we can exclude some variables and emphasize other variables in our model.
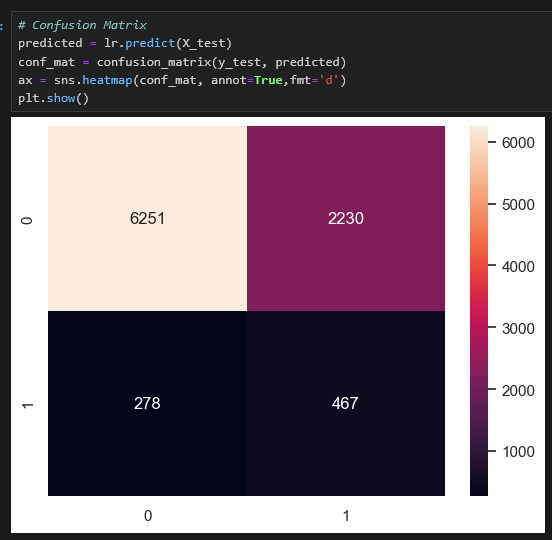
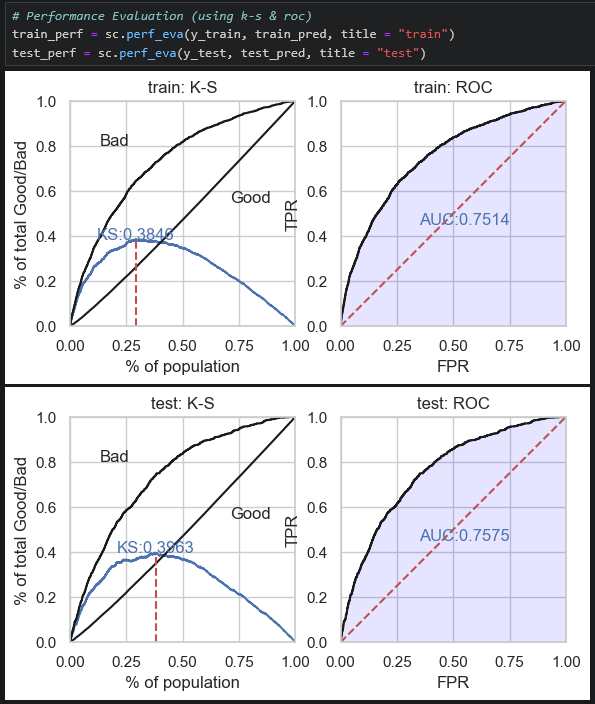
Examples